

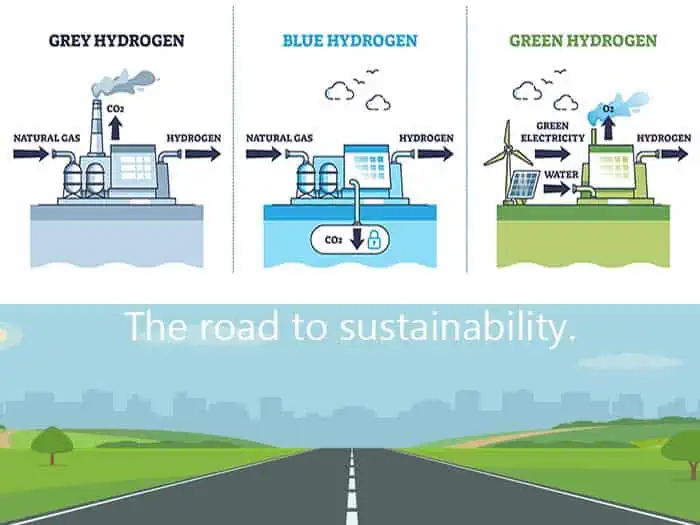
Green hydrogen is a clean fuel that produces only water when consumed in a fuel cell. Because it is produced from domestic resources, such as natural gas, nuclear power, biomass, and renewable power like solar and wind it is an attractive energy option for transportation and electricity generation applications.
SCS Engineers’ recent publication “Green Hydrogen – A New Frontier in Energy” evaluates the feasibility of hydrogen as green energy from production, transportation, storage, infrastructure investment, and environmental impact aspects. He discusses the technical and environmental challenges being addressed now through research, design, and development, and addressing the environmental obstacles to successful implementation of fuel cells and the corresponding hydrogen infrastructure.
Keep an eye on the Department of Energy’s Hydrogen and Fuel Technologies Office site where DOE publishes the developing and testing complete system solutions that address all elements of infrastructure and vehicle technology, integrated hydrogen and fuel cell technologies validations for transportation, infrastructure, and electric generation in systems using real-world operating conditions.
Additional Related Resources:
In August, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced nearly $34 million in funding for 11 projects that will support high-impact research and development to improve and produce biofuels, biopower, and bioproducts. These biomass resources, otherwise known as feedstocks, can be produced by municipal solid waste (MSW) streams and algae and converted into low-carbon fuels that can significantly contribute to the decarbonization of transportation sectors that face barriers to electrification, like aviation and marine.
Transportation accounts for approximately 30% of total U.S. energy consumption and generates the largest share of the country’s greenhouse gas emissions. Biofuels serve as a low-carbon alternative to petroleum and can also be used to produce carbon-heavy products like plastics, fertilizers, lubricants, and industrial chemicals.
Among the DOE recipients is a team led by Stephanie Lansing, professor in the Department of Environmental Science and Technology at the University of Maryland (UMD). Lansing is leading a consortium of scientists and industry partners to research innovative ways to use waste and to make value-added products that will contribute to the sustainability of our economy and planet.
SCS Engineers is an environmental engineering firm specializing in waste management and renewable energy from waste products. SCS is on the Lansing team focusing on biofuel production. The team includes Ohio State University, Mississippi State University, Virginia Tech, Idaho National Lab, and Quasar Energy Group. Their first task is to conduct a waste characterization study across every U.S. region during every season of the year, to understand how location and the time of year affect landfills’ incoming waste. The results help determine what the biofuel potential of that waste is.
Another Lansing team will be working toward producing bioplastics that are made without using fossil fuels and degrade much more easily than current plastic products.
The biofuel and bioplastic projects involve sustainability and economic assessments comparing them to current products on the market to see how marketable these new products can be. And the reason why Lansing’s comprehensive teams are important; they will help commercialize any new products.
Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm stated in the DOE August 3 press release, “The companies and universities leading these projects will ensure that our cutting-edge biofuel technologies reduce carbon emissions, create new jobs up and down the supply chain, and are made in America by American workers.”
More information about Solid Waste Management and Biofuels.