

The ABA 54th Spring Conference on Environmental Law, March 26 – 28 in Philadelphia, PA., is where you join leading environmental, energy, and resources law professionals for knowledge-sharing, networking, and inspiration. The conference provides timely, topical updates on the latest opportunities and challenges facing the field of environmental law, with a deep dive into the fields of environmental compliance, energy, and resources law. Join – SEER – the Section of Environment, Energy, and Resources, to learn about the latest developments shaping the practice today and the long-term trends that will drive the future.
At the ABA 54th Spring Conference you will be able to engage in lively discussions with top practitioners, including environmental consultants, in-house counsel, and prominent scholars, as they tackle today’s most pressing legal challenges. The conference kicks off with plenary sessions examining critical issues such as Justice Alito’s reshaping of environmental jurisprudence and the evolution of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks. A special track of panels will explore the practical and legal complexities of navigating PRP groups, negotiating contracts in the PFAS era, and managing Clean Water Act Section 404 permitting. Sessions will also cover federal-interstate compacts and the legal intricacies of environmental compliance in a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape.
Panels will address cutting-edge topics like natural resource damage litigation, regulatory pathways for emerging contaminants, and the intersection of environmental criminal enforcement and climate-related challenges. Discussions will provide practical approaches to balancing the energy transition with national security, while also diving into the ethical implications of working with environmental consultants. Insights into global ESG trends, the federal air toxics program, and practical applications of environmental justice will equip attendees with actionable strategies they can apply to their work.
For law students and young professionals, a dedicated panel offers career-focused advice and actionable guidance for navigating transitions within the legal field. This session will highlight practical pathways to building a fulfilling career while fostering connections within the industry.
Whether you’re a seasoned expert or just starting out in your practice, join us in Philadelphia to forge new connections, gain fresh perspectives, and find inspiration among your peers in environmental, energy, and resources law. This is your opportunity to learn, grow, and build meaningful relationships—all in the vibrant and historic setting of the City of Brotherly Love and Sisterly Affection.
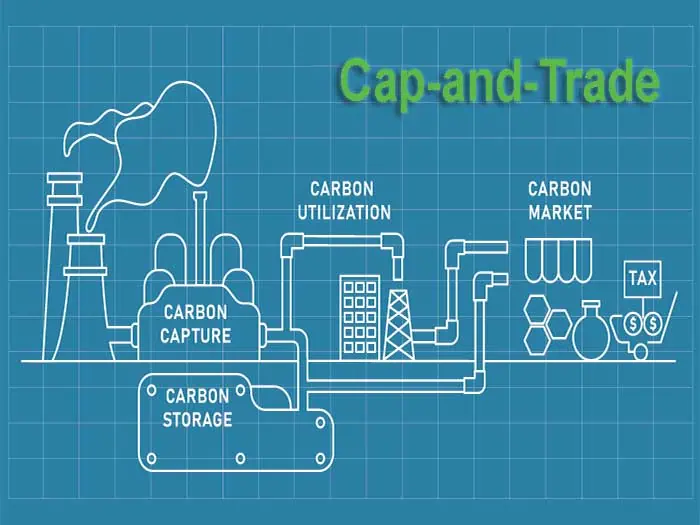
In our first Carbon Credit Series, we learned that there are two types of carbon markets: regulatory and voluntary. We covered the basics of the voluntary carbon market and shared a list of protocols that carbon offset project registries use for verification of Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emission reductions. We also covered the Organic Waste Composting Project protocol developed by the Climate Action Reserve (CAR) for voluntary carbon offset credits.
On our website you’ll find videos, presentations, blogs, and articles about carbon capture, storage, utilization, and the carbon market by our national experts and environmental professionals. Today, we direct you to a new paper by Erik Martig and Victoria Evans entitled The Cap and Trade Market.
The authors step you through the navigating the California cap and trade regulatory market for potential opportunities and pathways to credits. We hope you find the paper and additional resources valuable. As always, our writers and staff professionals are available to answer your questions or provide information specific to your industry, state, and goals.
About the Authors:


Additional Carbon Credit and Market Resources:
The 32nd Fall Conference, October 23-25 is an opportunity to hear from leading practitioners and to learn about the challenges and opportunities shaping environment, energy, and resources law. During the conference, you will be able to leverage professional development opportunities, connect with industry experts such as SCS Engineers, and stay informed about the latest trends.
The conference features engaging discussions with leaders in environmental, energy, and resources law, including state and federal regulators, leading scholars, and in-house counsel. Each day will kick off with a plenary session, such as exploring the emergence of AI and its implications for environment, energy, and resources law, and the impact of recent Supreme Court decisions.
The conference agenda is diverse, providing updates on the Clean Water Act and Clean Air Act. A hypothetical industrial accident will focus on managing key roles in responding to the accident. Attendees will gain an understanding from energy practitioners as they delve into environmental justice considerations and the permitting process for energy and environmental projects and the strategic siting of renewable energy projects. Climate change remains a pressing concern, and panel discussions will explore recent climate litigation and the ramifications of climate change on water availability. Hear from panelists as they address Tribal considerations in the areas of treaty rights and co-management of state and federal lands and natural resources. Additional topics to be examined include dam removal developments, contaminated waterways cleanups, the impacts of regulatory requirements on supply chain logistics, the emergence of contaminants such as microplastics and 6PPD, and the evolving landscape of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) and climate disclosure practices.
Experience firsthand this enriching event, where you’ll gain insights from top practitioners, build valuable connections, and be inspired by peers in the environmental, energy, and resources law community. We’ll see you in Seattle!
SCS Engineers’ professional staff, located according to their knowledge of regional and local geography, regulatory policies, and industrial or scientific specialty, are available nationwide. SCS professionals are technical experts and have been admitted as expert witnesses and supported legal counsel in a variety of environmental and regulatory litigation matters. We are always available to discuss:
The ABA Annual Spring Conference on Environmental Law, April 3-5 in Chicago, IL., is where you join leading environmental, energy, and resources law professionals for knowledge-sharing, networking, and inspiration in the Windy City. The conference provides timely, topical updates on the latest opportunities and challenges facing the field of environmental law, with a deep dive into the fields of environmental compliance, energy, and resources law. Join – SEER – the Section of Environment, Energy, and Resources, to learn about the latest developments shaping the practice today and the long-term trends that will drive the future.
What to Expect
Lively discussions with leading practitioners, including state and federal regulators, leading scholars, and in-house counsel. Each day will kick off with a plenary session diving into key topics: one on forthcoming Supreme Court decisions that could reshape environmental law, and one on the evolution of EPA’s enforcement tools. A special track of panels will focus on the challenges of regulating across multiple jurisdictions. Panels in this series will help attendees understand how state priorities shape Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act implementation, parse through competing frameworks steering the energy transition, and make sense of global ESG trends influencing U.S. policy. The conference will also feature a litigation workshop focused on cutting-edge strategies for using unique types of evidence, like Indigenous Knowledge, in the courtroom.
Panels will examine liability mechanisms for historical PFAS, explore how regulatory pathways for emerging contaminants will impact clients, and consider practical approaches to environmental justice through the lens of a real case study in Chicago. Top speakers will weigh in on balancing the energy transition against national security and the ethical implications of artificial intelligence for lawyers. In addition to insights and practice tips from top practitioners, two panels will begin with case summary presentations by law students and young attorneys that attendees can use in their own practices.
Whether you are an experienced practitioner or in the beginning stages of your practice, join us in Chicago to create new connections, exchange perspectives, and get inspired by your fellow environmental, energy, and resources law professionals.

This protocol applies to greenhouse gas reduction projects that divert eligible organic waste or agro-industrial wastewater streams that otherwise would have gone to uncontrolled anaerobic storage, treatment, and disposal systems (solid waste landfills, onsite anaerobic wastewater treatment facilities, etc.).
Projects that involve co-digestion of eligible organic waste streams with livestock manure are also eligible if they comply with the Livestock Project Protocol, diverting waste to a biogas control system (BCS). The protocol accepts several technologies, including:
Project Eligibility
The protocol stipulates the following requirements:
Project Exclusions
Protocol excludes the following activities:
Project Outcomes
A project is eligible to receive credits for ten years from the start date or until project activity is required by law. Applications for a second 10-year eligibility period are available. Only two AD facilities have registered with the Climate Action Reserve (CAR). CAR has awarded these projects a total of 224,655 CRTs, valued at approximately $700,000. In 2022, CAR awarded 22,257 CRTs to these projects. At a market price of $3.00/CRT, 22,257 CRTs have a value of $66,771.
Credit Feasibility
Understanding the technology and navigating protocol requirements can take time and effort. That’s where we come in. Contact SCS Engineers at service@scsengineers.com or Greg McCarron on LinkedIn to learn how your project may qualify.
Additional Resources

Carbon credits can be a reliable and lucrative source of revenue for organic waste management facilities in addition to more traditional revenue sources. Voluntary carbon credits provide compost and anaerobic digestion facilities with an additional source of income, complementing tipping fees and sales of final products. Carbon credits are issued, bought, and sold in carbon markets in a broader effort to lower greenhouse gas emissions. The Climate Action Reserve (CAR) establishes carbon credit standards, guidelines, and values (Climate Reserve Tonnes or CRTs).
Participation in voluntary carbon markets, mines, landfills, compost facilities, and anaerobic digestion facilities can generate additional revenue while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Is your project eligible for carbon credits?
There are two main types of carbon markets: regulatory and voluntary. Regulatory carbon markets require mandatory participation. Voluntary carbon markets provide carbon offset credits for qualifying products that effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions from a baseline level. Each voluntary market defines its baseline and qualifications for offset projects. Offset credits can then be sold. Within voluntary carbon markets, eligible organic waste management and landfill projects can participate in generating carbon credits.
Project developers can enter into purchase/sale agreements and single-year or multi-year partnerships with buyers to secure evaluated carbon prices. The project developer does not need to guarantee credit quantities, as the brokerage assumes responsibility for managing the credits over a specific period and guarantees a price per credit. The brokerage markets any amount exceeding the agreed-upon price per credit to potential buyers. This option provides more long-term pricing stability.
Climate Action Reserve (CAR)
CAR is a nonprofit organization that promotes the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through market-based policies and solutions. CAR serves as an approved Offset Project Registry (OPR) for the State of California’s Cap-and-Trade Program and is integral in supporting the issuance and administration of compliance offsets.
CAR also establishes standards for voluntary offset projects in the North American voluntary carbon market. It operates as a publicly accessible registry for carbon credits generated under its standards. CAR has eight voluntary offset protocols for waste handling and methane destruction projects in the United States, Mexico, and Canada. They assist, advise, and register clients with voluntary offset projects.
SCS has partnered with clients to pursue voluntary offset projects in Organic Waste Composting and Organic Waste Digestion protocols. Contact SCS Engineers at service@scsengineers.com or Greg McCarron on LinkedIn to learn how your project may qualify.
Series: Part II – Planning and Development of a Public Compost Facility
Series: Part III – Climate Action Reserve Organic Waste Digestion Project Protocol