


Conducting Phase I Environmental Site Assessments (ESAs) must navigate the complexities of fees versus liability to provide crucial services. Balancing these aspects is essential for mitigating future liabilities while ensuring thorough assessments during due diligence.
Environmental consultants face significant risks during Phase I ESAs. The potential environmental liabilities discovered often exceed the fees and profits from these assessments. Inadequately performed ESAs or overlooked environmental issues have led to substantial financial consequences for firms, sometimes amounting to hundreds of thousands of dollars. This highlights the importance of thoroughness and accuracy in these assessments to mitigate risk and protect the environment, the borrower or lender, and the consulting firm.
According to LightBox EDR’s historical data[1], the average fee for a Phase I ESA rose 11% from 2018 to 2023, with costs ranging between $1,400 and over $7,500. These variations reflect factors like the assessment’s complexity and the property’s characteristics.
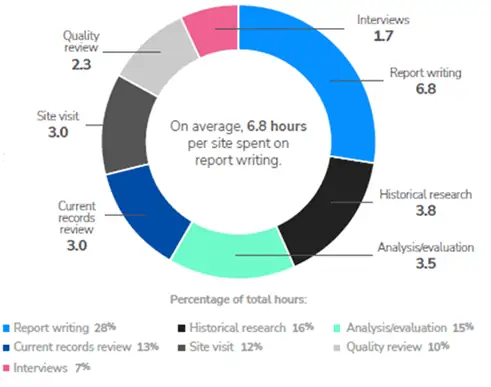
Report writing consumes the most hours in Phase I ESA-related tasks, LightBox EDR reports. The average hours per report across all aspects is twenty-five. A $75/hr. Consultant preparing the report costs $1,875, compared to $150/hr. Consultant at $3,625, not including profit and direct costs like travel, historical research fees, and regulatory fees. Investing more in a comprehensive ESA may be more cost-effective than missing a significant environmental issue.
Choosing a sub-$3,000 consultant for a Phase I ESA, regardless of the property’s apparent simplicity, could increase risks. Even straightforward properties can present unforeseen environmental challenges, affecting assessment accuracy and the project’s timeline and cost.
Firms conducting Phase I ESAs must adhere to professional standards like ASTM E1527-21 or local standards. Failing to meet these standards can lead to liability for missed or inadequately assessed environmental conditions.
The cost of a Phase I ESA reflects the required research and analysis, including a review of historical records, site visits, and potential environmental risk evaluation. Costs vary based on the expertise needed, especially for properties with complex histories or significant environmental issues and legacies.
Despite having professional liability insurance and contractual limitations of liability, firms can face significant business disruptions due to the time and expenses involved in litigation from oversights or inaccuracies in assessments.
Paying more for a Phase I ESA often results in a more comprehensive assessment. Higher fees enable exhaustive research, advanced technology use, and specialist engagement, leading to a thorough understanding of the property’s environmental status.
The fee for a Phase I ESA should align with the property’s specific complexities and risks. Industrial properties or those with hazardous material histories require more intensive assessment and review than simpler sites. However, low-risk sites can also reveal hidden environmental issues during assessments.
For example, a Phase I ESA on a rural property without apparent issues can become complex due to external factors like a neighboring gasoline tank leak. Such situations highlight the need for comprehensive and well-funded assessments to evaluate a property’s environmental status accurately.
The unpredictable nature of environmental risks emphasizes the importance of thorough and adequately funded Phase I ESAs to identify and address such risks effectively.
The implementation of ASTM E1527-21 in February 2023 introduced new considerations. This standard clarifies All Appropriate Inquiries (AAI) requirements and brings more precision to the assessment process. It mandates historical records for industrial properties, specific photographic and mapping requirements, and land title records detailing environmental liens or Activity/Use Limitations.
A notable update in E1527-21 is the approach to emerging contaminants. Until classified as a federal CERCLA hazardous substance, emerging contaminants like PFAS and PCB-containing building materials are optional in Phase I ESAs. This standard evolution reflects the dynamic nature of environmental assessments, where the cost of a Phase I ESA is a strategic decision to mitigate liability risks. Consequently, contaminants like PFAS and PCB-containing building materials, while not mandatory, can be included as a ‘non-scope consideration’ at the discretion of the Phase I ESA user.
While higher costs often lead to more thorough and reliable Phase I ESAs, balancing these costs with the property’s specific needs and risks is vital. The goal is a comprehensive understanding of environmental risks and conditions that support cost-effectiveness.
Investing more in a Phase I ESA is an investment in quality, risk management, and long-term cost-effectiveness, benefiting both the client and the consulting firm.
Phase I Environmental Site Assessments References:
Vapor intrusion is a regulatory hot button gaining traction on states’ radar nationwide. This is driven by a growing understanding of how vapors travel through the soil into structures, posing health risks to occupants, coupled with research showing volatile vapors can be problematic even at very low concentrations.
As in California, conservative assumptions by regulatory agencies call for careful due diligence during the assessment process. These salient concerns recently brought a real estate developer in Monrovia to seek a professional engineer.
The client plans to convert a commercial property to residential use. But before moving forward, it needs to assess potential environmental issues associated with the property. That’s where SCS comes in, drawing on its concrete knowledge base in geology and chemistry—and leveraging its grasp of regulatory requirements.
The work in Monrovia entails a detailed soil vapor assessment, looking for volatile organic compounds (VOCs); the discovery at this site came as little surprise to Julio Nuno, Senior Vice President, and Project Director, as these constituents are often found during evaluations of this kind.
Assessing for VOCs
In this case, the soil contained eight VOCs, some at non-compliant levels. The good news is, after an extensive, multi-step vetting process, Nuno and his team came up with a relatively inexpensive solution to tackle a potentially daunting problem.
“As part of the soil vapor assessment, we compare concentrations we find on-site to screening levels established by the Department of Toxic Substances Control. We often see levels in exceedance of regulatory thresholds, particularly in industrial areas with releases that can travel from groundwater to soil into the building through the slab,” Nuno says.
Most prominent at the Monrovia site were two chlorinated compounds that have been used as solvents in industrial applications: tetrachloroethylene, also called PCE, and trichloroethene, or TCE. PCE is commonly present in industrial settings and communities as drycleaners widely and routinely used the chemical for decades.
Nevertheless, the work begins even before confirming VOC levels and other specifics around these compounds. The first step is a Phase I Environmental Assessment looking to see if past use of the property or surrounding property may have left a significant environmental impact. The SCS team discovered the adjacent property had a release of VOCs they identified as a ‘recognized environmental condition,’ meaning it needs further evaluation using a Phase II to determine if vapors could migrate onto the client’s property.
During the Phase II Environmental Assessment –the collection of soil and soil vapor samples –the SCS team gets even more specific, determining what’s present, specific locations, what degree of contamination, and what these findings mean for redeveloping the property and its final use.
“We confirm subsurface concentrations and if they exceed state screening levels, and if the site represents a potential risk for future residential use. The information informs our possible solutions to mitigate any migration of certain VOCs into the building and the indoor air,” Nuno explains.
Redevelopment Goals – safety and cost containment
Safety comes first, but containing project costs is a priority, which comes down to knowing design options, how to piece components together with both function and economics in mind. At this site, achieving safety and controlling costs centered largely around looking at the mandatory infrastructure– a ventilation system for a planned underground parking garage to prevent accumulation of carbon monoxide and other vehicle exhaust emissions.
“We knew the underground parking would require a ventilation system. It makes sense to look at the parameters associated with that design to verify if it serves dual purposes to ventilate the garage and mitigate the potential for VOCs to enter the building,” Nuno says.
By studying air exchanges that would occur, the number of times replacing air-containing pollutants with cleaner air per hour, Nuno gets his answer. “We determined that a second, separate system would not be necessary for sufficient ventilation; the assessment enabled us to confirm vapors would not travel into the residential portion of the building.”
The client can save $50,000 to $75,000 in capital expenses upfront while achieving their safety goals and avoids ongoing operations and maintenance costs for added infrastructure.
An added layer of protection
Identifying the issues for site developers and their tenants, then plotting the best course of action to ensure safety and regulatory compliance takes experience and knowledge. SCS devises a soil monitoring plan, alerting developers of indications of potential contamination to the soil, of odor, or anything unusual that could suggest an environmentally adverse condition. The plan advises on how to respond should there be an unexpected condition adding a further protection layer.
“It’s essential that an engineer understand the applicable federal, state, and local standards for completing assessments, as well as understand regulatory stipulations. You must also know the variations in those stipulations to effectively design a sustainable plan,” Nuno says. “In Monrovia, we comply with the Department of Toxic Substances Control requirements, the requirements of the Los Angeles Regional Quality Control Board, and others. Each has specific stipulations for evaluating each contaminant. So, we stay on top of which rules apply to which location,” he says.
Nuno has submitted a draft report for review by his client and its legal counsel; he’ll meet with them to discuss findings and explain their meaning. SCS includes an executive summary, explaining in plain language what is salient; often, a backup report includes thousands of pages. “It’s a lot of complex information, so we work on the language,” Nuno says.
“It’s important to paint an accurate picture and use terms that all parties, whether the client, investors, or other stakeholders understand. These redevelopments are major projects with many due diligence considerations. We want to provide accurate findings and recommendations that the client and their advisors can digest to help them with their decision making.”
More resources:

Historic fill is common on properties that were once rural and have become prime redevelopment sites as communities expanded. The fill may include contaminated materials like foundry sand, ash, demo and construction debris, and even municipal waste. In the past, these materials were used to fill wetlands or change the grade of the property before initial development. Today regulations have evolved, and state agencies require property owners to manage these materials appropriately during redevelopment. Also, particular types of historic fill are often not robust enough to structurally support your new building.

There are many different kinds of fill materials – each with different physical properties and different potential contaminants. Knowing what is on your property before you start designing the site layout, and certainly, before you start digging, will help you plan your project to save time and money, and to receive state agency approval.
Before You Buy
The more you know about the property and the earlier you know it, the better prepared you will be to make decisions about how best to protect yourself from potential environmental liabilities and prepare for the environmental and geotechnical issues that historic fill can cause. Since every property is unique, the first thing you need to do is gain a thorough understanding of the property’s history and past use. Invest in a comprehensive Phase 1 Environmental Site Assessment (ESA). Consider it a starting point for clues about the possible types and amounts of historic fill which may be present on the property.
If the results of the Phase 1 ESA warrant it, conduct a Phase 2 ESA and geotechnical study to collect soil, fill, groundwater, and soil vapor samples. The Phase 2 ESA and geotechnical studies will help you understand if fill and contaminants are present and the best options for addressing them during the development planning stage.
Historic fill on a property is no longer the impediment to development that it once was. Take these steps to get ahead of potentially contaminated historic fill, and keep your project on time and budget.
By testing early, performing a proper geotechnical evaluation, and incorporating design adaptations where needed, you can successfully develop projects with historic fill within your schedule and without breaking your budget.
SCS professionals are available to answer questions or concerns you may have pertaining to commercial, residential, or private development on brownfields – we provide remediation, brownfields, and Environmental Due Diligence services nationwide. Contact or one of our experts.

Ray Tierney, PG, is a Vice President of SCS Engineers and one of our National Experts on Sustainability. He has 30 years of experience in environmental and sustainability engineering and has helped a wide range of organizations control and reduce their legacy environmental impacts and liabilities, lower their costs, obtain grants and permits to expand, and implement cost-saving practices. Ray serves the Midwest region and projects throughout the U.S.
JohnTabella, PG, LEED AP®, is SCS Engineers National Expert for Environmental Due Diligence and for Federal Services. In this capacity, he oversees all aspects of environmental services opportunities and projects primarily throughout the eastern seaboard and supports on opportunities and projects throughout the U.S.
Floyd Cotter specializes in solid waste management projects. His project work involves all areas of solid waste management including planning, permitting, transportation, landfill design, construction, and monitoring. Floyd is also experienced in general civil engineering, construction oversight, environmental site assessments, closure and post-closure plans, and permit and contract document preparation. Floyd is located in the Central region.
Randy Bauer has nearly 3 decades of experience conducting environmental site assessments, subsurface investigations, groundwater monitoring programs, soil and groundwater remediation, and geotechnical investigations at industrial hazardous waste and solid waste facilities. Randy is available to answer questions on the western seaboard.