

To generate a return on investment of site-specific GCCS, you need OMM staff who understand the strengths and weaknesses of your site. From that understanding, successful OMM teams and facility owners can design, perform, and fine-tune their program.
SCS’s BMP’s uses a “beyond the compliance OMM model” because the practice leads to strengthening relationships with regulatory agencies and LFG energy providers. Our clients expect to move toward a field optimization program when both OMM procedures and regulatory requirements are fine-tuned to work in concert. That investment pays dividends by increasing compliance and improving gas recovery. When developed OMM principles are defined clearly, and evolved along with GCCS design and construction, teams rise to the challenge, and the reward is a consistent track record of excellent GCCS operation.
Part 1 of the series discusses design considerations for landfill gas collection and control systems (GCCS); Part 2 takes into account construction quality assurance (CQA) measures during construction of GCCS; and Part 3 covers BMP’s for GCCS Operation, Monitoring, and Maintenance (OMM) in the September/October issue of MSW Magazine. The SCS Team covers:
A look at the confusion stemming from regulatory uncertainty of new rules limiting air emissions from municipal solid waste landfills by David Greene, P.E., SCS Engineers – Asheville, NC.
The landfill industry continues to work with EPA Administration to get a longer-term stay to work out needed NSPS/EG rule changes. At this time, industry representatives are hopeful both these related goals can be achieved.
While the new NSPS/EG rules became effective back in 2016, the concerns with the rules raised at the time still remain unresolved. Despite this, we can expect resolution though it may take some time to fix. The fog should be lifting, yielding changes that are expected to be more workable for both the landfill industry and state/local regulators. In the meantime, stay tuned and stay informed.
Read the full article with links to the NSPS/EG update in a recently published SCS Technical Bulletin.
SCS Engineers periodically prepares Technical Bulletins to highlight items of interest to our clients and friends who have signed up to receive them. Our most recent SCS Bulletin summarizes the new rules which took effect on October 28, 2016, with compliance obligations under the NSPS Subpart XXX rule beginning November 28, 2016. Originally, states and local air jurisdictions were to submit their proposed EG rules by May 30, 2017; however, there have been some delays in this process, which we condense and detail in this Bulletin. SCS will continually update coverage of this Rule on our website.
We continue SCS’s Advice from the Field blog series with guidance from an article in MSW Magazine by Daniel R. Cooper, Jason Timmons, and Stephanie Liptak.
The authors of a recent article in MSW Management Magazine present engineering ideas that provide for more efficient construction of a GCCS. Gas system operators will benefit by having fewer pumps to operate and maintain and shallower headers that are more easily accessible. Odor management will be easier along with other benefits.
Read the full article here to learn about the design elements for maximizing long-term benefits, impacting: bottom liners, location of the blower/flare station, leachate risers, extraction well targets, and external header piping.
Temporary Landfill Caps
Temporarily capping landfill slopes is becoming a common measure for landfill operators. There are many benefits to closing landfill slopes with geomembrane on a temporary basis. One of the benefits is delaying construction of the final cover. Following is a discussion of the steps that should be taken to determine whether temporarily capping the slope with geomembrane and postponing the final cover construction is a better financial/operational decision.
Cost Burden
Constructing the final cover is costly, and it is considered an unavoidable expense that has no return on the money spent. Therefore, some operators perform a financial evaluation to determine whether the final cover construction costs can be delayed (provided, of course, that such delays are acceptable to the regulating agency). When evaluating whether to delay the final cover, the cost of maintaining the slopes during the postponement period should be considered. The operator must look at the financial aspects of either closing the slopes with a temporary geomembrane or of leaving the slopes open during the postponement period.
Temporary Landfill Capping Option
The benefits of temporarily capping the slopes during the postponement period may include:
The other side of the coin is the expense associated with the temporary cap. There may be repair costs associated with the geomembrane every few years in order to ensure that the temporary cap remains intact.
Leaving Slopes Open Option
The option of leaving the slopes open during the postponement period involves maintenance expenses such as:
The benefits of leaving the slopes open are twofold: first, the operator will save the costs of constructing the temporary cap; and second, the operator will gain additional airspace as waste settles during the postponement period.
Experience with the Temporary Capping Option
As discussed above, both options provide the benefit of gaining additional airspace during the postponement period. Constructing a temporary cap involves the costs of materials and installation, including the geomembrane and the ballasting system that keeps the geomembrane in place. Generally, the financial and non-tangible benefits of a temporary cap that remains in place five years or longer are more attractive than leaving the slopes open; therefore, most operators choose to install a temporary cap. The next step in the financial evaluation should be comparing the costs of the temporary cap to permanently closing the slopes without postponement.
Final Step in the Financial Evaluation
The next question is whether it makes financial sense to postpone the construction of the final cover.
Waste settlement during the postponement period and the resulting airspace are considered the determining financial factor in choosing the right option. If the present worth value of the airspace generated from waste settlement during the postponement period is greater than the cost to construct the temporary cap at the present time, then the temporary cap option would make financial sense; otherwise, the final cover should be constructed without postponement.
It should be noted that the length of the postponement period plays a very important role in this financial equation. Longer postponement periods have the potential for a greater gain in airspace. Another incentive that should be factored into the financial evaluation is the potential return on the money set aside for the final cover construction during the postponement period.
To assist with this financial evaluation, landfill operators are encouraged to discuss these options with their landfill engineers. Settlement models can be performed to calculate the amount of airspace that may be generated during the postponement period as well as the present worth value of the generated airspace. The returns on the final cover construction costs during the postponement will just be “icing on the cake.”
Read the related Advice From the Field blogs from the landfill and LFG experts at SCS Engineers:
Contact the author: Ali Khatami or your local SCS Engineers’ office.
Getting a firm handle on a solid waste operation and expenses is a challenge for any solid waste agency manager or landfill operator. It is particularly imperative in this era of “lean and mean” budgets and looming regulatory policy. Doing more with less is the watchword for most operations across the country still reeling from the financial impacts of the Great Recession.
SCS Engineers has created a package of articles to help you identify if your landfill, landfill gas, or solid waste operation is ready for 2017. We hope this useful guidance will help you plan for the upcoming year. SCS professionals are always available to answer questions and provide advice. Find the office or SCS professional nearest to you by clicking on one the links here: Offices and Professionals.
Download, print or share this package by using the download button under the articles or by using the navigation at left. The package includes the following information written by SCS National Experts:
Article in Waste360: explains who’s impacted and how to begin managing the costs.
SCS Technical Bulletin: a digest of hundreds of EPA regulatory policy into the information and timelines to act on now.
Article: strategic financial planning to support infrastructure costs.
Call our compliance specialists – find the office nearest you or email us at
SCSeTools® gives you the ability to instantly map air leaks, vacuum distribution, wells that are “over pulling” and wells that are underutilized – valuable tools for every wellfield technician to maximize system performance beyond simple compliance tracking and reactive wellhead tuning.
As a field technician, you walk a fine line – tuning to a threshold, pulling as hard as you can, as safe as you can. When important data factors start to wander you need to troubleshoot quickly to keep collecting as much as gas as possible without over compensating and adjusting wellheads multiple times. SCSeTools® makes troubleshooting faster and more efficient by turning your data into maps identifying important conditions in the field and the wellheads that need tuning. Field technicians know how to balance the wellfield without killing bacteria and without diluting the gas.
A map of your field with your specific tuning range quickly shows data that are typically missed in reams of data. SCSeTools alerts you to these indicators using a map of each wellhead in the wellfield. Where you formerly needed months for these changes to become apparent, SCSeTools tells you at the touch of a button when a change began occurring and which wellheads are impacted. As a technician you know what you need to tune and which wellheads need your attention.
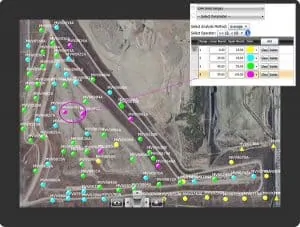
Using SCSeTools pick any parameter that the GEM collects and create custom ranges or use specified guidelines to quickly identify trends throughout the landfill. Tuning ranges can be adjusted to specific conditions found at individual landfills. Smooth a saw tooth collection pattern and learn from your data for maximum vacuum and maximum collection without risk.
…and as waste settles, it can have an effect on equipment,” according to Pat Sullivan of SCS Engineers in this ClimateWire article. As the U.S. EPA focuses on pushing landfill owners into cutting down on methane emissions some worry that a combination of tightening regulations and poor cost analysis might put some smaller landfills out of business.
LANDFILL EMISSIONS: Going to the dump? You might make electricity
Kavya Balaraman, E&E reporter
Reprinted from ClimateWire with permission from E&E Publishing, LLC. Copyright 2016.
An informative and complete discussion from Jeffrey L. Pierce of SCS Engineers, Energy Practice of siloxanes and landfill gas (LFG) utilization. Plus, presentations on the economics and performance of siloxane removal from biogas; advice on siloxane sampling, analysis and data reporting recommendations on standardization for the biogas utilization industry.