

According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), and the World Health Organization (WHO), noise is a serious health concern in the 21st century. Although Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is seemingly the least expensive and simplest control for noise, PPE is also the least effective. It relies on personnel to utilize the correct PPE at the appropriate times.
Approximately 22 million workers are exposed to hazardous noise levels each year in the United States, and over 10 million US workers have diagnosed Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL). (1) Industries with high numbers of workers exposed to loud sounds include construction, agriculture, mining, manufacturing, utilities, transportation, and the military. Excessive noise can lead to a range of health problems for all citizens, but a growing number of non-industrial workers, including restaurant and school employees, are experiencing this irreversible occupational hazard.
Noise in U.S. industry is an extremely difficult problem to monitor, acknowledges Craig Moulton, a senior industrial hygienist for OSHA. “Still,” he says, “OSHA does require that any employer with workers overexposed to noise provide protection for those employees against the harmful effects of noise. Additionally, employers must implement a continuing, effective hearing conservation program as outlined in OSHA’s Noise Standard.”
Sounding Out Realistic and Effective Solutions
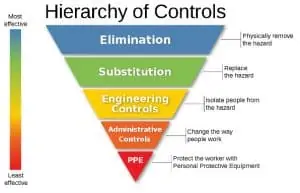
SCS Engineers Industrial Hygienists utilize the hierarchy of controls when developing solutions that involve elimination, substitution, and engineering controls as the first steps to controlling excessive noise. Only when a solution cannot be identified or implemented from these controls do we look to administrative controls and PPE.
“When we design our investigations and remediation plans to address specific noise issues, we are also sensitive to the costs associated with expensive analytical testing,” states Jed Douglas, Industrial Hygiene National Expert. We find cost-effective and lasting solutions by:
SCS has completed numerous noise investigations and sampling for various facilities, such as schools, offices, warehouses, industrial and commercial buildings. SCS’s Industrial Hygienists help building owners, facility engineers, property managers, attorneys, insurance companies, and municipalities with investigations and remediation of the factors contributing to excessively loud noise, including area sampling and surveys of personal exposure for regulatory compliance. We can also help with hearing protection programs, medical monitoring programs, and the selection of PPE.
Additional Information
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on human or animal life activity. Machines, transport, and propagation systems mainly cause outdoor noise sources worldwide, including highways; construction activities; urban congestion; power generation; public transportation, recreational vehicles, home power tools, yard maintenance, and air cooling equipment.
Common sources contributing to harmful industrial loud noise:
Health effects from loud noise include:
When Doug Doerr got a call from a Colorado-based landfill operator with a hot gas probe at his site’s boundary, Doerr’s day kicked into high gear. Chasing down gas migration problems is nothing new in an SCS client manager’s life, but that reality makes the job no less complex. And in this scenario, he was dealing with a site that he occasionally got called to visit, so to understand the problem fast, he needed the site’s historical data and the current information to fully picture what was happening.
Doerr started with basic landfill gas information from the client: the monitoring probe’s location and a drawing of the gas collection system to determine where the probe was in relation to the gas system. But as you know, that is one small slice of a king-sized pie.

“I queried our in-house landfill gas technical group (engineers, geotechnical experts, and field personnel). And got over 25 responses within several hours with suggestions, one of which came from Ken Brynda in SCS Field Services, who leveraged DataServices to help me identify and narrow down the potential cause of the problem,” recalls Doerr.
DataServices, a module of the SCS eTools® digital platform, collects, stores, manages and analyzes large volumes of continuously accumulating landfill gas data for individual sites or multiple landfills. The module provides a quick method to view landfill gas scenarios.
The beauty of it is that it generates maps and charts to visualize every well and every probe. These system components are viewed in relation to one another and in relation to the perimeter, where the methane on that Colorado site flowed. Further, SCS Field Services’ landfill gas gurus, such as Ken Brynda, plug-in specific parameters that keep a close watch on any well or a group of wells.

As responders viewed initial results from their respective bases around the country, Brynda churned out more information in a few hours, running point charts to capture the balance gas, methane, flow, temperature, supply vacuum, and the vacuum applied to each well. He looked for trends that narrow down cause and point to solutions.
Eliminating the Possibilities – Rule Out Well System Malfunctions
“It can take days if we’d had to do it the old school way with spreadsheets laid out in a lot of rows. But we could identify the potential problem in a matter of hours, backed by a comprehensive evaluation for the landfill operator in eight hours,” Doerr says.
When Field Services staff work to solve a problem with a probe, they look for an outlier, something from a group of wells that’s not behaving like the other wells. In this case, Brynda determined that the wells near the hot probe were functioning properly. DataServices eliminated potential problems by slicing through and analyzing large chunks of data confirming the system was working efficiently.
Next, we observed that the wells are likely too far away to pull gas back from waste, adjacent to the probe in question, where there are no wells.
“DataServices helped rule out malfunctions, and that’s a big deal because if you can confirm the landfill system is working properly, you have narrowed your focus and can look toward other possibilities, ultimately leading to corrective options,” Doerr says. Brynda and Doerr suggested putting in temporary wells in that area to avoid odor migration and health and safety issues.
Doerr continues watching the situation and is prepared with a several-point action plan to mitigate exceedances and avoid falling out of compliance. “We continue watching the data to ensure the gas collection system continues to function well. Should there be issues again, we’re able to fully identify the gas migration pathways and anything in the system that looks out of the ordinary,” Doerr says.
If the client decides to add wells in time, data from the expanded infrastructure will be added to the app and monitored. “As the number of wells grows, DataServices grows with it, adding any, and as much, monitoring and collection data as the operator wants. DataServices will always be in the background to monitor, collect and analyze LFG data in real-time, whenever we need it,” he says. Being able to store, organize, dissect and analyze unlimited volumes of information from one location is powerful. And not just because it helps operators identify problems as they are happening, but because it and our teams can support them in looking for trends over time. Keeping an eye on the activities that keep the systems in balance is less costly.
For Doerr, who spends time in the field but longer hours with his clients, DataServices and the ability to interact quickly with experts like Brynda help SCS deliver more value to clients. “As much as I’d love to master DataServices, I need to focus all of my time on my clients’ business and goals; having support from Field Services and DataServices makes us all more efficient.”
Landfill Technologies and Comprehensive Expertise
SCS eTools® and SCS DataServices®, now with SCS MobileTools® for viewing data and charts anywhere; available to pull landfill data into DataServices for analyzing. You can customize and focus on exactly what you need fast. As Doug and Ken emphasize, it’s info that you likely already have, but may not be able to use quickly for troubleshooting.
SCS RMC®, remote monitoring and control of landfill equipment and systems.
Comprehensive Landfill Services
On March 1, 2021, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) proposed several amendments to air quality regulations pertaining to the regulation of New Jersey Hazardous Air Pollutants (NJHAPs) as well as fumigation operations. The NJHAP regulations changes could significantly impact MSW landfills because they include proposed changes to hydrogen sulfide regulation as a NJHAP.
Key changes are summarized as follows:
Several potential implications could result from these proposed changes, including:
A virtual public hearing regarding the proposed changes is scheduled for April 8, 2021, at 4:00 PM (ET). A link to the virtual public hearing will be posted at http://www.state.nj.us/dep/aqm/curformp.html.
Written comments are due no later than April 30, 2021, to www.nj.gov/dep/rules/comments.
Please direct questions to your SCS Project Manager or one of our local professionals:
Our industry is in a period of a rapid transition to digital data management, but particularly on landfills. Often you read that the latest technology, whether by a brilliant programmer or rolling out as part of a takeover, is innovative. Linking technology and innovation is becoming commonplace, but they are not the same. Innovation is a human process requiring experimentation and iteration to solve landfill issues that often have nothing to do with computers or mobile phones. Landfill technology or apps are tools.
Innovation takes a team of diverse expertise, different perspectives with a constant desire to learn, and most importantly, the primary desire to make landfill operations more efficient and safe. Innovators use technology when and how it makes sense to improve environmental management, profitability, and care for employees and the local community. Lower cost solutions for the vast amount of data collection completed faster and without human error come from people with hands-on in-the-field experience. When it comes to landfill technology, its value is clear when a landfill practitioner demonstrates how the particular technology fits into a solution. The nice part is they also get to the point and skip the tech-speak and jargon.
The Landfill Technology Evolution Started Here in 2003
Back in 2003, SCS couldn’t find technology that would enable our engineers and technicians to support landfill operations as we desired. Proving the proverb “necessity is the mother of invention,” we developed a database for our use. Its value in the field was immediate, and SCS continued to adapt and develop SCS DataServices® and SCS MobileTools®, basing refinements on each landfill and client need. It took people in the waste industry to make the right technology tools for the industry.

Meet Oliver Early, SCS’s DataServices and MobileTools Product Manager. Oliver started his career managing landfill operations. He became interested in technology because it got results for him as a landfill manager of 15 facilities. By combining a comprehensive investigation of physical landfill systems, such as landfill gas collection and control and other environmental monitoring and control systems with evaluations of compliance areas, he improved his landfill system performance and substantially increased power plant production. He used multivariate data techniques, including time series and network analysis, to scrutinize and refine results. Merging DataServices capabilities under Oliver’s guidance took SCS’s original internal database to a timesaving product for all landfills, not just the landfills SCS operates.
The platform, called SCS eTools®, includes modules for leachate, groundwater, DataServices, and the newest application SCS MobileTools, free for those using DataServices. The technology is currently in use on over 630 landfills nationwide and benefits all of SCS’s design, build, and operations work.
For example, if methane readings at a gas probe are elevated, that’s an indication of a potential LFG migration issue. While expertise is great – it could take hours to diagnose and mitigate. With DataServices, you could run an evaluation of the existing well field in a few minutes, ruling out issues with current wells. With the touch of a button, you can share the information with your team and focus on potential mitigation recommendations.
Remote Monitoring and Control Technology Didn’t Happen Overnight Either
The best and most innovative solutions come from combining the stakeholders’ experiences and thoughts. Let’s meet a few of the people who lead other landfill innovations.

In addition to being a licensed drone pilot herself, flying over 100 landfills, Business Manager Melissa Russo uses SCS Remote Monitoring and Control (RMC) technology to support her landfill clients. Her contributions increase safety and lower environmental risk using unmanned aerial vehicles to gather field data at a lower cost. Melissa developed SCS’s national drone and geographic information systems (GIS) programs to respond to her clients’ needs for expensive regulatory and operating challenges. As a result, capturing more (methane) greenhouse gas instead of releasing it into the atmosphere provides the obvious environmental benefits, and landfill personnel have better and safer working conditions.
Depending on the sensor or camera attached, her pilots can monitor methane concentrations using a tunable diode laser, measure and map surface temperatures to mitigate elevated temperature conditions, or create topography, aerial imagery, and estimate filling volumes. Operators can view, detect and measure changes over time, gaining insight into critical infrastructures such as water infiltration, liquid flow, and vegetation distributions. Melissa’s use of GIS provides a low-cost solution to data management and sharing between field and office.
Melissa is an innovator who genuinely cares about our industry, taking the time to listen and truly understand her clients’ challenges and long-term goals. Only then does she devise customized solutions, regardless of whether it uses technology or not. See Melissa at work.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is Bang for Your Buck

SCS RMC’s Business Manager is David Hostetter. His experience includes remote monitoring and controls systems engineering, construction, and operation; landfill gas and leachate engineering; and mechanical engineering. Dave’s focus is on automating remote process control of landfill systems, landfill gas blower/flare stations, wellfield vacuum and flow, along with leachate and groundwater pumping systems, weather equipment, and air monitors.
As a landfill gas engineer, his impetus was to avoid production downtime and keep operations within regulatory mandates. He wanted his clients to see what was happening at any given time and be alerted to atypical conditions. As a landfill engineer, he knows that “prevention is better than cure,” as long as it’s cost-effective. Dave’s solution is to leverage the Internet of Things through SCS RMC systems. Each piece of equipment you want to monitor gets a sensor. His team configures each sensor or group of sensors to parameters based on his operator’s business needs and environmental reporting responsibilities. A local wireless network communicates with a base station providing continuous readings from each sensor.
RMC sends alerts if readings are outside an acceptable range or if an environmental threshold is nearing exceedance. Alerts go to the landfill’s designated staff or technicians via smartphones, computers, or tablets. From these devices, users access their interface to control, start, stop, and reset field systems and analyze system operation. They can also view data, graphs, tables, alarms, and reports.
That’s more than convenience; it saves labor dollars spent to diagnose and reset these systems and is especially valuable for remote landfills. By design, clients can enable custom authorization levels for their systems. Naturally, the analytical tools are easy to use, understand, and report, as he explains in his video.
Albert Einstein Said…
“You can’t solve a problem on the same level that it was created. You have to rise above it to the next level.” We’re not comparing ourselves to Einstein, but all three SCSers leading their teams know that compliance policy never stops changing, and landfills are unique beasts made up of complex systems that need balance to perform. Performance is based on daily decisions and landfill readings generating enormous amounts of data. SCS’s job is to make your job better by collecting those millions of data bits for analysis faster, helping landfill operators use the intelligence to identify the cause and appropriate response to hundreds of issues that are part of landfill or facility management.
The backbone of every service at SCS Engineers is to design and develop based on our clients’ specific needs. As innovators, our mission is to leverage proven technology to meet those needs. As our founders did, we strive to understand our clients’ current and future needs, then develop or integrate the appropriate technology to meet those needs.
SCS is one of the most experienced and successful environmental compliance, design-build, operations, and maintenance firms in the United States. No stand-alone technology company can substitute for our knowledge and hands-on experience with innovative landfill design, build, and operations.
Visit SCS Engineers to discover SCS eTools and SCS RMC capabilities. You’ll find case studies, technology awards, and more resources for using technology to manage labor, liquids, air monitoring, groundwater, volume, GHGs, and more
Stephanie Taylor’s outstanding work recently earned her the prestigious Air & Waste Management Association’s 2021 Young Professional Award. As an SCS Engineers Environmental Professional, Stephanie manages and supports numerous clients in the Midwest, providing valuable air compliance/permitting and groundwater compliance services. She is a respected colleague at SCS and frequently provides services to offices outside of her business unit as an air compliance/permitting specialist.
In her recent work, Stephanie provided air compliance/permit audit services to a private client completing a companywide multimedia audit. Her work took her to multiple industrial manufacturing plants nationwide. Her attention to detail is integral in identifying non-compliance and areas of improvement that her client implemented company-wide to improve operations and compliance with permit requirements.
Stephanie joined with Midwest AWMA board in 2016 and quickly accepted the challenges of leadership, becoming Vice Chair in 2018 and as Chair for the Midwest Section in 2019 and 2020. In both positions, she was responsible for managing/coordinating the annual Midwest AWMA conference, a big job. She continues to serve the Midwest AWMA Chapter in a leadership role.
Stephanie has been the lead for the Young Professionals (YP) group in the SCS Kansas City office for several years. Her responsibilities include coordinating YP networking events and coordinating with the corporate YP group to support and mentor new YPs entering the workforce.
Tia Jeter, Stephanie’s manager says,
I have full confidence in Stephanie and her abilities and do not hesitate to let her take the lead on projects as I know the work quality she produces. She is a dedicated and key member of our SCS team. She is technically very strong and dependable, and co-workers know she will get the job done and stay on top of the client’s needs. She has done a great job getting involved with both SCS groups, the YP association, and the AWMA board.
EPA is releasing the interim guidance for public comment. The guidance provides information on technologies that may be feasible and appropriate for the destruction or disposal of PFAS and PFAS-containing materials. It also identifies needed and ongoing research and development activities related to destruction and disposal technologies, which may inform future guidance.
The interim guidance addresses PFAS and PFAS-containing materials including:
The agency is also providing guidance on testing and monitoring air, effluent, and soil for releases near potential destruction or disposal sites. EPA’s interim guidance captures the significant information gaps associated with PFAS testing and monitoring and identifies specific research needs.
The interim guidance is intended to assemble and consolidate information in a single document that generally describes thermal treatment, landfill, and underground injection technologies that may be effective in the destruction or disposal of PFAS and PFAS-containing materials.
As further research and development occur on this issue, EPA will incorporate this increased knowledge into future versions of this guidance to help decision-makers choose the most appropriate PFAS disposal options for their particular circumstances. EPA will review and revise the interim guidance, as appropriate, or at least once every 3 years.
See the EPA website: EPA Interim Guidance on Destruction and Disposal of PFAS.
Instructions: All submissions received must include Docket ID No EPA-HQ-OLEM-2020-0527 for this rulemaking. Comments received may be posted without change to the Federal eRulemaking Portal. You may send comments by any of the following methods:
According to Waste Dive, the document is the first such federal guidance on the destruction or disposal of PFAS or PFAS-containing materials. It describes the available science used in three major techniques: deep well injection, landfilling and thermal treatment. Acknowledging uncertainty about potential environmental effects, the EPA proposed the interim storage of PFAS-containing waste until further research can “reduce the uncertainties associated with other options.”
Industry groups such as the National Waste & Recycling Association (NWRA) and the Solid Waste Association of North America (SWANA) said they are analyzing the document and discussing with their members, such as SCS Engineers what the interim guidance means for daily landfill operations. The trade groups will submit comments on the document by the Feb. 22 deadline.
SCS periodically prepares Technical Bulletins to highlight items of interest to our clients and friends who have signed up to receive them. We also publish these on our website at https://www.scsengineers.com/publications/technical-bulletins/.
Our most recent Bulletin entitled EPA Seeks Feedback On Inactive Surface Impoundments at Inactive Electric Utilities summarizes the EPA’s request for comments and information pertaining to inactive impoundments at inactive facilities.
Operators and owners who may be affected by forthcoming decisions around inactive CCR surface impoundments include electric utilities and independent power producers who generate CCR within the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) code 221112. Though the EPA states “other types of entities … could also be regulated” and advises those wanting to confirm if the regulation applies to them to read the applicability criteria and comment. Landowners with a legacy surface impoundment on their property purchased from a utility will want to review the proposed definitions closely.
SCS Engineers will continue to post timely information, resources, and presentations to keep you well informed. These include additional guidance, industry reaction, and webinars for our clients.
Visit our website for more information.
SCS Engineers announces Brittney Odom’s promotion to the Southeast region’s Environmental Services Director. Odom will continue expanding and integrating SCS’s environmental engineering and consulting operations to provide more streamlined and efficient services in her new role. She will lead environmental operations in Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Georgia, and the Caribbean. As with all SCS leaders, she continues serving her clients in Boca Raton in her expanded role.
Odom supports real estate developers, municipalities, banks, and insurance firms to identify properties’ environmental conditions. Next, depending on soil, water, and geotechnical testing determines the appropriate environmental due diligence and the engineering activities necessary to redevelop them and be in 100% compliance with local and federal rules.
There is an active push to develop more affordable residential housing in the U.S. Real estate developers and residents want to be close to business and transportation hubs, but potential development sites could require remediation. Once agricultural sites, golf courses, or at one-time housing industrial operations, these properties need environmental testing, due diligence, possibly remediation, or vapor intrusion barriers to ensure the safe redevelopment. No matter the condition, properties with a past can return to pristine condition and make desirable residential and mixed housing locations, supporting economic development.
“It’s important to know and understand all of the options ahead of time to keep costs down and environmental quality up for sustainable communities,” stated Odem. “You need to reassure all parties that there is no leaking storage tank or anything that could compromise health.”
Her focus recently is on the redevelopment of large-size properties contaminated with arsenic and other legally applied pesticides. These property types include golf courses and agricultural land that have become inactive but are in high demand for residential use. These projects may need soil management, including remediation, soil blending, and placement restrictions.
Odom has years of experience conducting environmental site assessments, overseeing remediation activities, and submitting regulatory reports, including Phase I & II assessments in Florida, Tennessee, Louisiana, Texas, and the Caribbean. These focus on gas station properties and bulk storage terminals for large oil companies, often located on prime waterfront sites.
Additional highlights in Odom’s professional career include expertise in the applicable Florida Regulatory Chapters and Standard Operating Procedures. She also has experience in state and international cleanup efforts and their associated regulatory procedures. She participated in successful environmental closure efforts, with imposed engineering controls and property restrictions.
Odom has ten years of experience managing subsurface investigation and conducting oversight during remedial activities, including source removal and remediation system installation. She holds certifications in 40-Hour HAZWOPER/OSHA training, Loss Prevention System, CPR, RCRA Hazardous Waste, DOT Hazardous Waste, and American Petroleum Institute certification.
“Brittney’s breadth of experience solving the complexities of large scale redevelopment while meeting all environmental regulatory compliance enables her to innovative better solutions,” said Carlo Lebron, SCS vice president and director of SCS’s Southeast operations. “She’s an expert, with access to our deep bench of engineers, scientists, technology, and even economists within SCS.”
SCS Engineers now provides the Augusta Environmental Services Department with engineering, environmental and testing, and Construction Management & Quality Assurance Services at the Deans Bridge Road Landfill, in Blythe, Georgia. The facility operates under the State of Georgia Environmental Protection Division as a Subtitle D Landfill, accepting up to 1,500 tons per day of waste. Active and closed sections of the landfill comprise approximately 1,177 acres of property. Some additional acreage contains ancillary facilities such as office and maintenance buildings, customer drop off area, sediment ponds, roads, and leachate holding facilities. The Augusta Department of Environmental Services is responsible for the landfill facilities, solid waste management planning for Augusta, and all residential solid waste collections. Additionally, the Department is responsible for the Augusta Brownfield program and other environmental compliance issues.
Landfills are carefully engineered facilities closely regulated and monitored to ensure they have the protections necessary to prevent contamination of groundwater, air, and adjoining land. Best landfill management practices include collecting and treating leachate – the water that passes through a landfill. The methane gas naturally produced from decomposing landfill waste is collected and converted into various forms of energy – including compressed natural gas. This alternative fuel powers Augusta Solid Waste trucks or is a substitute for pipeline natural gas.
The Department consolidated all landfill services assigning them to SCS Engineers, a professional environmental consulting firm with over 50 years of experience in performing landfill site acceptability studies, landfill design services, landfill environmental compliance activities. The firm was already engaged in the Landfill’s Gas Collection and Control System (GCCS) expansion. The consolidation of services provides a more cost-effective approach for permitting, design, operations, monitoring, and maintenance. The comprehensive SCS team is a uniquely qualified and experienced full-service consulting and engineering team with demonstrated relevant field experience in Georgia. Leading the team is Sowmya Bulusu, a Georgia Professional Engineer, with over 12 years of landfill engineering performed in accordance with the Environmental Protection Division (EPD) of the Georgia Department of Natural Resources, the Georgia Solid waste management Act, and other applicable federal, state, and local rules and regulations. As the Project Director, Carlo Lebron is a registered Georgia Professional Engineer for 15 years bringing over 21 years of experience on over one hundred solid waste projects.
“The SCS team brought the five-year permit review submittal package in early, giving Georgia’s Environmental Protection Division plenty of time to deem it administratively complete,” stated Sowmya Bulusu. “Working with our field technicians, we quickly identified and brought at-risk gas wells into compliance, used our drones to provide an aerial survey of the entire landfill, saving Department funds.”
SCS Engineers’ environmental solutions directly result from our experience and dedication to solid waste management and other industries responsible for safeguarding the environment. Click for more information about comprehensive landfill services.
From SWANA’s Executive Summary
A new report developed by the SWANA Applied Research Foundation (ARF) addresses two important questions associated with municipal solid waste (MSW) at landfills.
What tasks will be required to manage closed landfills following the post-closure care period to ensure continued protection of public health and the environment?
How will those associated costs be paid for?
Subtitle D regulations require that the post-closure care period is maintained and the environmental protection systems are managed and monitored—it should be 30 years in length, but the period is determined by the state regulatory agency that issued the landfill permit. Once the post-closure period ends, the closed landfill enters into a new status, which SWANA defines as the “Long-Term Management,” or LTM period. EPA’s Subtitle D regulations don’t address monitoring and maintenance activities required during this period.
Based on the ARF’s research, the new report offers conclusions regarding the long-term management of MSW landfills during the LTM period. Some include best practices, but ARF also had some interesting conclusions related to final cover geomembranes and looking to landfills as longer-term assets.
The full report, The Long-Term Management of Closed MSW Landfills Following the Post-Closure Care Period, is currently available only to SWANA ARF subscribers. SWANA members receive free access to ARF industry reports one year after publication.
Contact your SCS Engineers Project Manager or local office for information on best practices.