

SCS Engineers provides a free guide to the most common environmental reports due at the federal and state levels. Each guide includes an overview of the reporting due along with the date each state requires submission.
When SCS says free, we mean it. No need to submit your company name, no endless email trail will follow; these are free guides to download and share with others from the compliance experts – SCS Engineers.
Click to download or share each state guide:
If your state is not listed, contact the nearest SCS office to speak with a compliance professional in your area and in your business sector; SCS is nationwide.
If you have questions or need help sorting out details such as which reports apply to your business or step-by-step support on how to prepare your reports in the states listed above, contact our regional professionals.
Learn more about Ann
Ann O’Brien 1-773-775-6362
Learn more about Cheryl
Cheryl Moran 1-608-216-7325
Getting a firm handle on a solid waste operation and expenses is a challenge for any solid waste agency manager or landfill operator. It is particularly imperative in this era of “lean and mean” budgets and looming regulatory policy. Doing more with less is the watchword for most operations across the country still reeling from the financial impacts of the Great Recession.
SCS Engineers has created a package of articles to help you identify if your landfill, landfill gas, or solid waste operation is ready for 2017. We hope this useful guidance will help you plan for the upcoming year. SCS professionals are always available to answer questions and provide advice. Find the office or SCS professional nearest to you by clicking on one the links here: Offices and Professionals.
Download, print or share this package by using the download button under the articles or by using the navigation at left. The package includes the following information written by SCS National Experts:
Article in Waste360: explains who’s impacted and how to begin managing the costs.
SCS Technical Bulletin: a digest of hundreds of EPA regulatory policy into the information and timelines to act on now.
Article: strategic financial planning to support infrastructure costs.
Call our compliance specialists – find the office nearest you or email us at
SCSeTools® gives you the ability to instantly map air leaks, vacuum distribution, wells that are “over pulling” and wells that are underutilized – valuable tools for every wellfield technician to maximize system performance beyond simple compliance tracking and reactive wellhead tuning.
As a field technician, you walk a fine line – tuning to a threshold, pulling as hard as you can, as safe as you can. When important data factors start to wander you need to troubleshoot quickly to keep collecting as much as gas as possible without over compensating and adjusting wellheads multiple times. SCSeTools® makes troubleshooting faster and more efficient by turning your data into maps identifying important conditions in the field and the wellheads that need tuning. Field technicians know how to balance the wellfield without killing bacteria and without diluting the gas.
A map of your field with your specific tuning range quickly shows data that are typically missed in reams of data. SCSeTools alerts you to these indicators using a map of each wellhead in the wellfield. Where you formerly needed months for these changes to become apparent, SCSeTools tells you at the touch of a button when a change began occurring and which wellheads are impacted. As a technician you know what you need to tune and which wellheads need your attention.
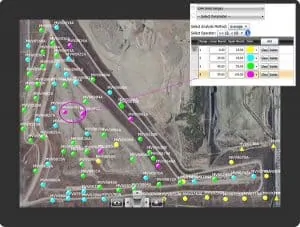
Using SCSeTools pick any parameter that the GEM collects and create custom ranges or use specified guidelines to quickly identify trends throughout the landfill. Tuning ranges can be adjusted to specific conditions found at individual landfills. Smooth a saw tooth collection pattern and learn from your data for maximum vacuum and maximum collection without risk.
Last year Tom Barham, SCS Engineers’ General Counsel and Field Services Construction Director made headlines at SCS with his admission to the United States Supreme Court Bar. We are extremely proud of Tom!
This month Tom had the opportunity to have lunch with Supreme Court Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg as part of a fireside chat sponsored by the Association of Corporate Counsel. The discussion was led by Ted Olsen, a former Solicitor General of the United States who has argued 62 cases before the Supreme Court.
Justice Ginsburg was remarkably open and candid about her career and generous with her advice, including sharing advice from her mother in law on how to have a successful marriage, which she noted as “the best advice she ever received.”
As a pioneer in women’s rights and civil rights in America, Justice Ginsburg was involved in many important cases as an advocate and a judge. Asked about which cases stood out, she recalled a case challenging Virginia Military Institute’s (VMI) male only cadet policy. She noted that this was one case Mr. Olsen lost 7-1 and the one vote he got was from Justice Scalia who was already was on VMI’s side and needed no more advocacy to secure his opinion. (According to Mr. Olsen, RBG is known for her “wicked sense of humor”.) The case was memorable not for its legal precedent, but because of correspondence from the family of a female cadet. The female cadet’s father, a Marine and VMI graduate, wrote Justice Ginsburg to thank her for helping to create the opportunity for his daughter to attend VMI.
Subsequently, another letter from the daughter arrived with a Keydet pin which the daughter received upon graduation. The pin traditionally is given to the mother of the graduate, but since the cadet’s mother passed away before her graduation, the cadet sent it to Justice Ginsburg explaining that the Justice was like the grandmother to her and all future generations of female cadets. Justice Ginsburg keeps the letter and pin on her desk at the Supreme Court.
On how to have a successful marriage, Justice Ginsberg’s mother in law advised that it is best sometimes to be deaf to things you don’t want to hear, and handed her a pack of earplugs. Justice Ginsburg explained she has found that advice very helpful, choosing to be deaf to unpleasant things sometimes said.
“When you think about it, it was remarkable to have an opportunity to have lunch with a sitting Supreme Court Justice,” said Tom. “I even had an opportunity to ask for her advice on teaching fundamentals of the Constitution and our legal system to the international students in the class I teach in the University of Maryland Graduate School of Civil Engineering. Maybe I can get The Notorious RBG to guest lecture next semester?”
About Tom Barham
Mr. Barham is SCS Engineers General Counsel and Senior Vice President of Construction Services. He is a member of the Virginia and District of Columbia bars, and holds a degree in building construction. He has over 30 years of experience in construction and construction law.
Mr. Barham provides SCS Field Services with expertise in construction management, including procurement, scheduling, budgeting, and estimating, as well as other contract formation and administration activities.
Mr. Barham has directed several full service (design/build) projects and has been involved in numerous projects such as Landfill Gas (LFG) collection systems (blower/flare stations, extraction wells, horizontal collection trenches, header lines, and condensate collecting/containment systems); groundwater pump and treat systems (stripping towers, recharge galleries, groundwater wells, deep recharge wells, collection/distribution piping, and pump stations); bio-treatment facilities (containment areas, moisture/nutrient application, and soil mixing); underground storage tanks (excavation, testing, triple rinse, and restoration); soil vapor extraction systems (cat/ox treatment facilities, vapor extraction wells, collection header lines, and air make-up wells).
“This program directly supports the county’s Roadmap to a Sustainable Waste Management Future by helping businesses to implement recycling programs,” says Leonard. “And not only recycling but waste reduction, as well, all of which, of course, contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, resource management and sustainable materials management.”
Read the article about L.A. County’s Plan for Sustainable Waste Management
For years, Wisconsin landfills have relied on compliance with the storm water (stormwater) management requirements in the Chapter NR 500 code series to achieve compliance with the NR 216 storm water standards. Effective June 15, 2016, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) changed their policy, and now requires landfills and associated non-commercial borrow sites to obtain separate industrial storm water permit coverage.
Read the SCS Engineers Technical Bulletin to determine what action you may be required to take and by what date.
If you have questions or need help filing or developing a plan, please contact:
Betsy Powers, PE
(608) 216-7347
Sherren Clark, PE, PG
(608) 216-7323
…and as waste settles, it can have an effect on equipment,” according to Pat Sullivan of SCS Engineers in this ClimateWire article. As the U.S. EPA focuses on pushing landfill owners into cutting down on methane emissions some worry that a combination of tightening regulations and poor cost analysis might put some smaller landfills out of business.
LANDFILL EMISSIONS: Going to the dump? You might make electricity
Kavya Balaraman, E&E reporter
Reprinted from ClimateWire with permission from E&E Publishing, LLC. Copyright 2016.
Recent direct communications with SWRCB and local Regional Boards’ have indicated that during the 2016-2017 permit cycle year, inspections will be more detailed for facilities considered to be at high risk, which were specifically named as those with a long history of water quality violations, as well as scrap metal recyclers, and End-of-Life Vehicle (ELV) recycling. There will also be increased focus on facilities that discharge to impaired waterbodies with adopted Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) requirements.
Industries should take action now if there is any uncertainty in regards to the meeting permit regulations. Contact your local SCS Engineers’ office or one of our industrial stormwater experts in California, Cory Jones or Jonathan Meronek. If you need questions answered, or if you are unsure of your business’s requirements, and believe that your facility may be in violation, SCS will help sort through the permitting red-tape. This includes SMARTs filing, NOI/NEC or NONA submittals, SWPPPs and Monitoring and Implementation Plans.
Recent News, Stats, and Resources
More Resources
An informative and complete discussion from Jeffrey L. Pierce of SCS Engineers, Energy Practice of siloxanes and landfill gas (LFG) utilization. Plus, presentations on the economics and performance of siloxane removal from biogas; advice on siloxane sampling, analysis and data reporting recommendations on standardization for the biogas utilization industry.