

Navigating the Permitting Process for CCR Impoundment Closures and Groundwater Monitoring Systems
Join us on Monday, July 27 from noon to 2 p.m. CDT to learn how SCS Engineers helps electric utilities overcome permitting obstacles at CCR impoundments and landfills. We offer the service nationwide.
Using case studies, we’ll highlight the permitting process and the keys to how electric utilities overcame obstacles to achieve the results they needed.
What you can expect to learn?
Registration and USWAG conference information here. This year’s event is a series of webinars USWAG is offering at no additional charge for members and affiliates.
Partial Reprint of EPA Press Release
Over the past three years alone, EPA has assessed 6,572 properties, completed cleanups at 638 properties, and made 2,900 properties ready for anticipated reuse. Over this same period, more than 43,000 jobs have been leveraged as a result of Brownfields’ actions.
EPA recently announced the selection of 155 grants for communities and tribes totaling over $65.6 million in EPA Brownfields funding through the agency’s Assessment, Revolving Loan Fund, and Cleanup Grant Programs. Many of the communities and tribes selected can potentially assess or clean up brownfield sites in census tracts designated as federal Opportunity Zones.
“Without redevelopment opportunities, urban and rural communities – even those with deep historic roots – can eventually wither,” said OLEM Assistant Administrator Peter Wright. “Brownfields remediation and revitalization support communities by investing in the redevelopment of existing properties in the community.”
Since EPA’s Brownfields Program began in 1995, it has provided nearly $1.6 billion in Brownfield funding to assess and clean up contaminated properties and return blighted properties to productive reuse. EPA’s Brownfields funding has leveraged more than $32.6 billion in cleanup and redevelopment from both public and private sources, which in turn has produced more than 167,000 jobs. This is an average of nine jobs per $100,000 of EPA investment and more than $17 in private funding for each dollar of EPA Brownfield grant funding.
Brownfields grants have been shown to:
Background:
A Brownfield is a property for which the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse may be complicated by the presence or potential presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant. The Brownfields program empowers local leaders and communities to transform underused and distressed properties into community assets across America. Brownfields funds assess and cleanup vacant, underused, and potentially contaminated properties so that property can be reused as housing, recreation, and open space, health facilities, social services, or commercial sites. There are estimated to be more than 450,000 Brownfields in the United States.
For more information on successful Brownfields program applications, site revitalization, and success stories nationwide visit Brownfields and Voluntary Remediation. If you’d rather jump right into a few success stories, click on these below:
Locate a Brownfields and remediation expert near you – SCS Staff
Are You Ready to Respond to a Spill? is Part II of the SCS Engineers SPCC series. Click to read Part I here.
Imagine you get a late-night call informing you that a transformer at one of your substations has failed, and as a result, 8,000 gallons of mineral oil spilled. Your next decisions are critical to timely industrial spill response, and taking the right steps will put you on a path to minimizing the environmental impact and your company’s liability. Do you know how you would respond?
If your facility has over 1,320 gallons of oil, your required SPCC Plan should contain spill response steps. If your facility has less than 1,320 gallons of oil, you may not have written spill response steps at all. Whether or not your facilities have SPCC Plans, consider the following tips, so you’re prepared for that late-night call.
Play Where Will a Spill Go?
If a spill occurs at one of your facilities, do you and your employees know where the spill will go? It’s typically easy to track flow paths at facilities in rural settings, but it can still be tricky if the site is pretty flat. Facilities in urban settings can be much more difficult to track. Sure, the spill will go into that storm sewer inlet 100 feet away from the transformer, but where will it go from there?
Critical hours can be lost during a spill because the response team is pulling manhole lids to determine the path of the spill. A little time spent upfront to determine where a spill would go can save a lot of time and headaches.
So take a peek down that inlet grate to see where the pipe goes. Or give a call to the local municipality. Many have GIS databases mapping the storm sewer system, and they can help determine the correct flow path that a spill would take. Knowing where to deploy your spill response materials is a critical step to spill response.
Conduct a Mock Spill Drill
Try conducting a mock spill drill, so your employees understand your spill response procedures, where you keep spill response materials, and how to deploy those materials. Running through these items on a PowerPoint slide is a good start, but you can’t beat the hands-on activity of actually opening up the spill kit and laying down some boom. A spill drill can also help you identify potential issues with your planned response techniques.
Review Your Spill Kits
Spills kits, especially those stored in maintenance shops, are prone to dwindling inventories over time. While raiding the spill kit to wipe up a few drops of oil isn’t a bad idea, it is important to replenish the spill response materials for an emergency. Make sure your spill kits are stocked by keeping an inventory list taped to the top of the spill kit or just inside the lid. Check the spill kit against the inventory list regularly and replenish missing items. Each spill kit should include personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriate for handling the types and amount of chemicals that the kit is expected to control. PPE should be in good working order. Replace any PPE that is expired or showing wear.
It is also important to understand that absorbent materials come in many styles and work in different ways. Teach your oil-handling employees when to use granular absorbent, or pads and mats, and the proper way to lay booms and socks to prevent spills from seeping through the cracks. If you use “oil-only” absorbents, help employees understand the situations in which these are preferable over a universal absorbent.
Know When You Need to Call for Help
Do you know when you will call for outside spill response assistance versus what your staff can handle internally? The answer can vary by facility type, spill scenario, the experience level of your staff, and spill response materials and equipment that you have available. It’s important to think through different scenarios and know your internal capabilities and limitations, and when you need to call a spill response contractor.
Do you know who you will call? And do you have an agreed-upon response time established with the contractor? Depending on your facility’s location, it could take hours for a spill response contractor to reach the site. Knowing that lag time will help you plan for steps that your internal resources can take until the spill response contractor arrives.
Don’t let spill preparedness slip down your to-do list again. Use these techniques, so you are ready when the next spill occurs.
Jared Omernik has 12 years of experience helping electric utility companies with environmental compliance. Jared has extensive experience helping companies with SPCC compliance and SPCC Plan preparation. For questions about the SPCC Rule or spill response or preparedness, contact Jared at or find the nearest Environmental Engineers on our website.
An American Public Works Association (APWA) publication,
No single waste management approach is suitable for managing all materials and MSW streams in all circumstances. The USEPA hierarchy places emphasis on reducing,
reusing, and recycling as key to sustainable materials management. Citizens and elected officials are often surprised how technically complex solid waste management is, and once aware of the basics they better understand the associated costs. Responsible Solid Waste Management with colorful infographics and easy-to-grasp explanations, helps readers understand solid waste management from beginning to end.
The concept of integrated solid waste management is increasingly being used by states and local governments as they plan for the future. This management practice includes the source reduction of certain MSW streams and the recovery of generated waste for recycling or composting. It also includes environmentally sound management through combustion with energy recovery and landfilling practices that meet current standards or newly emerging waste conversion technologies.
Available on the APWA website or reach Michelle Leonard (co-author) or an MSW engineer nearby contacting SCS Engineers at .
Learn more about Sustainable Materials Management here.
From The Atlantic, Family Section
I, too, had a more-than-passing interest in the garbage truck as a kid; with palpable residual excitement, I can remember peeking through the window shutters of my parents’ front room to watch the vaguely menacing robotic arm jut out, snatch our garbage can, and dangle the can upside down over its back while the trash tumbled out. Why generations of kids have been so transfixed by the trash pickup, though, remains something of a mystery. So I asked parents, kids, child-development experts, waste-management professionals, and even the creator of a kids’ show about an anthropomorphized garbage truck for their insights. Together, we made our way—more aptly, lurched and rumbled our way—toward a unifying theory of why kids are so wild about garbage trucks.
Author ASHLEY FETTERS talks to several experts and the two foremost authorities—kids and garbage-truck drivers. Naturally, we never lost our fascination with the men and women in our industry.
Landfills located in areas with high precipitation usually experience leachate seeps on slopes. The location of leachate seeps varies, and the reason behind the seeps appearing on the slopes varies as well.
As long as the slope does not have its final cover, you can attempt to control leachate seeps no matter where the seep location. There are many remedies known to landfill operators for controlling seeps before the final cover, but leachate seeps below the final cover are not controllable. The reason is the seeps are out of reach, and you have no means to control or mitigate the situation. The only potential solution is a seep management system built under the final cover geomembrane at the time of final cover construction.
For landfills with slopes extending up to the top of the landfill without terraces, construct a leachate toe drain system (LTDS) at the toe of the slope adjacent to the landfill perimeter berm. The design will collect and convey liquids emanating from seeps further up on the slope (below the final cover geomembrane) to the leachate collection system. See Figure 1.
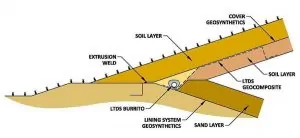
For landfills with terraces on the slope, construct LTDSs at every terrace. Best practices call for the location at the toe of the slope, above the terrace, the lowest point of that slope. Consequently, the terrace width prevents seep liquids from flowing further down the slope, and the LTDS at the terrace prevents the accumulation of leachate behind the final cover geomembrane at the interior line of the terrace. See Figure 2.
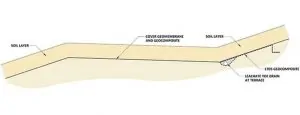
At the lowest point of the terrace, locate a downspout to convey liquids to the leachate collection system at the bottom of the landfill. You will also need a LTDS at the toe of the slope adjacent to the landfill perimeter berm, as discussed above. You may connect the terrace downspouts to the LTDS located adjacent to the perimeter berm to drain the liquids collected at terraces.
To prevent erosion of fines by small streams of liquids flowing down the slope below the final cover geomembrane use this best practice. This design will prevent depressions forming in the top surface of the final cover. First, place a LTDS geocomposite panel from the source of any leachate seep that you identify on the slope right before the construction of the final cover. Connect the panel to the LTDS pipe-gravel burrito at the terrace or perimeter berm. This solution provides a preferential path for liquids coming out of the seep without causing erosion. See Figures 1 and 2.
Place the LTDS geocomposite below the LTDS burrito when simultaneously constructing the burrito and the LTDS geocomposite. When constructing the LTDS burrito ahead of time, place the LTDS geocomposite above the burrito later. In either case, the contact area between the LTDS burrito and the LTDS geocomposite must be free of soil, which could impede the free flow of liquids to the LTDS burrito.
SCS has a 20-year record of accomplishment solving leachate seeps below the final cover geomembrane. Feel free to contact our landfill designers for advice.
About the Author: Ali Khatami, Ph.D., PE, LEP, CGC, is a Project Director and a Vice President of SCS Engineers. He is also our National Expert for Landfill Design and Construction Quality Assurance. He has nearly 40 years of research and professional experience in mechanical, structural, and civil engineering.
Learn more at Landfill Engineering
Dr. Gomathy Radhakrishna Iyer joined SCS Engineers in April 2019 as a Staff Professional working out of our Reston, Virginia office. She recently had the honor of delivering a presentation at the Global Waste Management Symposium in February. Learn more about Gomathy and her work as an engineer at SCS:

Tell us about your responsibilities as a Staff Engineer at SCS Engineers.
What attracted you to work at SCS?
What is your favorite part of working at SCS?
What do you feel is your greatest achievement/contribution at SCS?
What was your greatest challenge at SCS, and how did you overcome that?
What advice do you have for students who have recently graduated and are entering the engineering field?
You recently made a presentation at the Global Waste Management Symposium. Tell me more about it, and how did it go?
What are your hobbies outside of SCS?
Landfills are complex systems with many pipes for liquids and landfill gas running in many different directions. Some of these pipes are at the bottom of the landfill, such as leachate collections pipes, leachate toe drain pipes, pressure release pipes, etc. Other pipes are near the final cover system, either below or above, and closely interact with the final cover geosynthetics. Many of these are for control of landfill gas or leachate seeps at the landfill surface. Pipes may include vertical gas wells, horizontal gas wells, condensate sumps, condensate force main, compressed air lines to gas well pumps and condensate sumps, seep control sumps, electric conduits to condensate sumps and seep control sumps, leachate recirculation force main, stormwater downchutes, etc.
When pipe locations are near the final cover geosynthetics, below or above, or penetrating the final cover, design plans should show details of how the pipes or associated components interact with the final cover components. Lack of sufficient information may cause difficulties years later when scheduling the construction of the final cover. Most often, it becomes evident that many of the pipes constructed years earlier are too short for extending through the final cover.
Another aspect of piping and their interaction with the final cover is conflicts among different pipes, more specifically conflicts among gas pipes and liquid carrying pipes, in and near the final cover system. Liquid carrying pipes may include stormwater downchutes, rainwater toe drain pipes, and leachate toe drain pipes. Stormwater downchutes are usually large diameter pipes extending from the top of the landfill to the perimeter stormwater system. Rainwater toe drain pipes – pipes that receive water from the final cover geocomposite drainage layer, and leachate toe drain pipes – to collect leachate seeps below the final cover geomembrane, are co-located at terraces on slopes and the toe of the slope near the perimeter berm.
A few design considerations can be useful as guidelines during the preparation of design sets to address the relative position of these pipes and the final cover geosynthetics or to avoid conflict among pipes.
The complexity of landfills varies from site to site, and issues related to conflicts among gas and liquids pipes, and pipes and final cover geosynthetics vary depending on the geometry and other landfill features involved at each location. The best way to resolve conflicts before construction is to have a coordinated effort among parties involved in the design to discuss and find solutions to every conflict at the design stage.
About the Author: Ali Khatami, Ph.D., PE, LEP, CGC, is a Project Director and a Vice President of SCS Engineers. He is also our National Expert for Landfill Design and Construction Quality Assurance. He has nearly 40 years of research and professional experience in mechanical, structural, and civil engineering.
Learn more at Landfill Engineering
Leachate seeps from relatively wet landfills are a fact of life for some operators. Leachate seeps increase in intensity and frequency after a storm, and you’re wondering, how many seeps today; are they reaching the stormwater ditches, detention ponds, or wetlands?
We all deal with daily job challenges, but why not prepare better for this particular problem, given the consequences? Sitting back and waiting for a seep to appear and then scrambling to come up with a solution is obsolete and can be costly.
The timing of handling leachate seeps is as vital as submitting compliance data to regulatory agencies on time. Rapid mitigation of leachate seeps is essential before it turns into a compliance issue and exposing yourself to scrutiny by regulators. We all know that no compliance officer at the corporate office wants to hear from a facility the news of another compliance issue. To get a handle on managing leachate seeps, today’s operator has an arsenal of controls suited for different stages of a landfill’s operation. These controls may vary from the dry season to the wet season, as well.
As the landfill operator, you review the facility operation plan prepared by your engineer from the back to the front to make sure the document addresses all operations. The same document can also include descriptions of seep management controls. You simply request written solutions from your engineer, incorporating controls and guidelines into your operations plan. Your staff now has immediate means to combat the problem following the site operator’s direction using these pre-established guidelines.
With the controls in your facility operations plan, regulatory agencies won’t need to ask for the information. The operations plan has put forward a set of guidelines for the management of leachate seeps in your operations plan, and they became aware of these guidelines during the review of your document submitted to their office as part of intermittent or a renewal submittal. Inspectors are aware that your staff follows the guidelines when necessary; otherwise, non-compliance issues arise. Having an inspector observe a seep closing in on a stormwater ditch isn’t going to do much for your landfill’s standing. The regulators are well-informed and understand leachate seep prevention. They will work with you during the implementation of remediation measures based on the guidelines in the facility operations plan.
A reliable engineer will suggest, even emphasize, these measures to clients. You, as the operator, are not only prepared, but your site engineer and staff are too. Significant unexpected expenses associated with managing leachate seeps are a thing of the past, and inspectors can be confident that your management of leachate control is appropriate.
About the Author: Ali Khatami, Ph.D., PE, LEP, CGC, is a Project Director and a Vice President of SCS Engineers. He is also our National Expert for Landfill Design and Construction Quality Assurance. He has nearly 40 years of research and professional experience in mechanical, structural, and civil engineering.
Learn more at Landfill Engineering
The men and women of the solid waste industry have been continuing their jobs throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. In recognition of their hard work and sacrifice, SWANA is collaborating with Glad to support sanitation workers across the United States and Canada personally affected by COVID-19 through the Sanitation Workers Support Fund (Fund). The Fund is providing financial assistance to eligible front-line solid waste and recycling collection workers in the United States and Canada adversely impacted by COVID-19.
“The solid waste industry is considered essential, and its workers have been on the front line, without failure, making sure waste is collected and disposed of since the onset of COVID-19. This fund is an important recognition of their contribution to our communities, and is a way of providing support when they are personally impacted by the pandemic,” stated Suzanne Sturgeon, Health & Safety Program Manager for SCS Field Services and SWANA Safety Committee Chair.